
Réparer Windows
FIX corrupted files
sfc /scannowchdsk : réparer les erreurs de disque
chkdsk C: /F /Rbootrec : réparer le démarrage de Windows
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
bootrec /rebuildbcd

Link: https://www.malekal.com/bcd-boot-configuration-data-windows
Method 2. How to repair Windows 10/11 using DISM
Windows 10/11 includes a command-line utility known as DISM (Deployment Image Servicing and Management). DISM command Windows 10/11 can be used to repair and prepare Windows images, including, Windows Setup, Windows Recovery Environment, and Windows PE. Also, DISM can be used to fix the recovery image within an installation of the operating system.
To repair Windows 10/11 using DISM commands:
To check whether there is any corruption, Run command line as administrator, then type the following syntax and press "Enter".
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /CheckHealth
To scan the Windows image for any corruption, type below command and hit "Enter".
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /ScanHealthTo fix Windows image, type the following command and hit "Enter".
DISM /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:repairSource\install.wim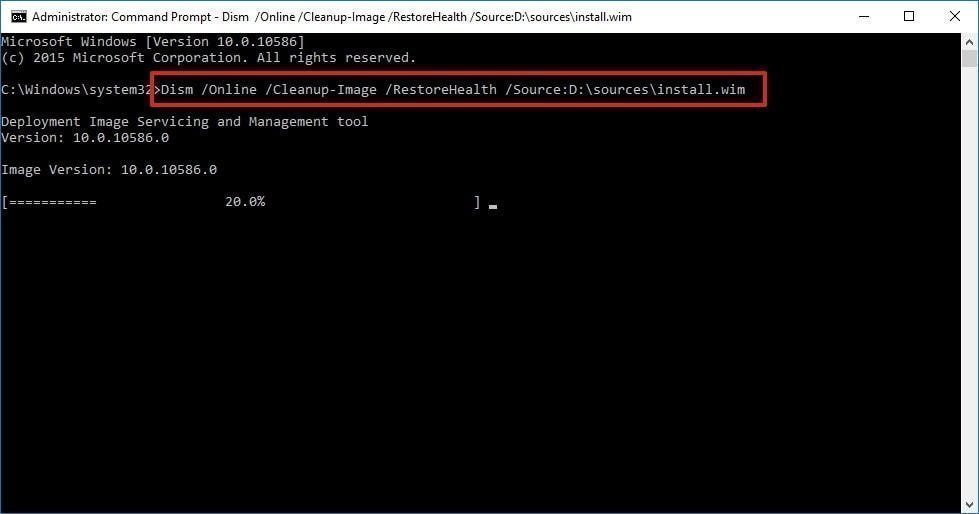
REMOVE DLL
RIGHT click on the START button and select WINDOWS TERMINAL (ADMIN)
You can then list all of the drivers on your computer using pnputil /enum-drivers and find the one with WDCSAM64_PREWIN8.SYS or you can just look at the error message.
In my case the driver that needs to go is OEM26.INF
Uninstall the driver using pnputil /delete-driver oem
You do NOT need a reboot so you can immediately retry to enable CORE ISOLATION and you should see a prompt to reboot once Core Isolation > Memory Integrity is turned ON.
GOD MODE
create directory with name:
GodMode.{ED7BA470-8E54-465E-825C-99712043E01C}
Restore PRG after boot
Restore Menu explorateur Windows 11
1. Utilisez Windows + S pour ouvrir la barre de recherche, tapez « cmd » et sélectionnez Exécuter en tant qu'administrateur.
2. Entrez la commande suivante dans la fenêtre de caractères de l'invite de commande et appuyez sur Enter pour exécuter la commande.
reg add HKCU\Software\Classes\CLSID\{86ca1aa0-34aa-4e8b-a509-50c905bae2a2}\InprocServer32 /ve /d "" /fCommande reg add
Note : Si vous souhaitez retrouver le menu contextuel ayant le nouveau style de Windows 11, veuillez exécuter la commande suivante dans CMD :
reg delete "HKCU\Software\Classes\CLSID\{86ca1aa0-34aa-4e8b-a509-50c905bae2a2}" /f.ref: https://www.ubackup.com/fr/windows-11/windows-11-afficher-plus-d-options-par-defaut.html
BLOAT WINDOWS
iwr -useb https://git.io/debloat|iex
